"Nylon composite sheet" in a bonded connection with Durethan |

| | | Tepex® continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites and their processing suitable for large-scale production. |

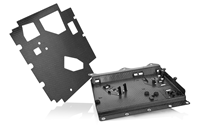 | | Example of a hybrid structure with nylon composite sheet |
Tepex stands for a material group of fully impregnated and consolidated, sheet-like composite semi-finished products made of high-strength continuous fibers (or long fibers in the case of Tepex flowcore) and a thermoplastic matrix. These so-called organic sheets can be processed into complex components in short cycle times by heating and subsequent forming. Continuous fibers are mainly glass and/or carbon fibers in the form of woven fabrics or other textiles. Matrix materials are thermoplastics such as polypropylene, polyamide 6, polyamide 66 and polyamide 12, polycarbonate, thermoplastic polyurethane and polylactide. The strengths of Tepex can be summarized as follows:
| - high stiffness
- high strength
- high lightweight potential due to low density
- short cycle times for component production
- thermoplastic matrix enables overmolding and welding
- high freedom of molding
- solvent-free
- recyclable as a material
- high energy absorption behavior
- low coefficient of thermal expansion
- good dimensional stability, chemical resistance and corrosion resistance

The combination of Tepex with short- or long-fiber-reinforced plastics with the same or a compatible matrix system and their processing method injection molding and compression molding also offers the excellent possibility of combining material and structural lightweight construction, e.g. by molding of:

- stiffening and stabilizing ribs
- force transmission elements
- functional elements
- dge sealing of the component

With suitable material selection and process control, a component is obtained with a material-to-material bond between the two components.
A basic distinction is made between a two-stage and a single-stage hybrid process. Both processes combine the following advantages:

- greater freedom of shaping
- Possibility of integrating additional functions and thus reducing subsequent steps
- combination of material and structural lightweight design
- short cycle times
- reproducible and fully automatable processes
- well established production technology

In hybrid molding (two-stage), on the other hand, forming of the organic sheet and injection take place together in the injection mold. The clamping unit of the injection molding machine serves as the forming press. The mold, which thus has to perform various tasks, must be specially designed for this process. In order to produce molded parts without reworking, the organic sheet semi-finished products are provided as near-net-shape blanks. These blanks represent a drape-compatible unwinding of the part to be produced, which can be calculated by means of the drape analysis.
Comprehensive information on all forming methods currently used for processing Tepex can be found in our brochure "Information for Processors" and on our homepage tepex.com.
Of course, we always remain for your disposal for a personal discussion about your individual project.

| Additional information |  | Tepex - Innovative composites | website | company website |  | press releases | media | company website |  | Tepex - Advanced thermoplastic composites | brochure | TechCenter |  | Tepex - Information for processors | brochure | TechCenter | | | | | |  | nylon composite | search | TechCenter | | | | |

